“Discover the international standards for cyber security, including ISO/IEC 27001, and learn about global frameworks, compliance, and best practices to protect your information and manage cyber risks effectively.”
In today’s digital age, cyber security is more crucial than ever. With data breaches and cyber threats on the rise, understanding international cyber security standards is essential for organizations worldwide. This blog will explore these standards, focusing on ISO/IEC 27001, various cyber security frameworks, and global regulations. By the end of this post, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the best practices and strategies to protect your information and manage cyber risks effectively.
Understanding International Cyber Security Standards
International cyber security standards are a set of guidelines and best practices designed to help organizations safeguard their information systems. These standards provide a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). The goal is to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
ISO/IEC 27001: The Gold Standard
ISO/IEC 27001 is perhaps the most well-known international standard for cyber security. It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information so that it remains secure. This standard includes requirements for implementing security controls tailored to the needs of individual organizations.
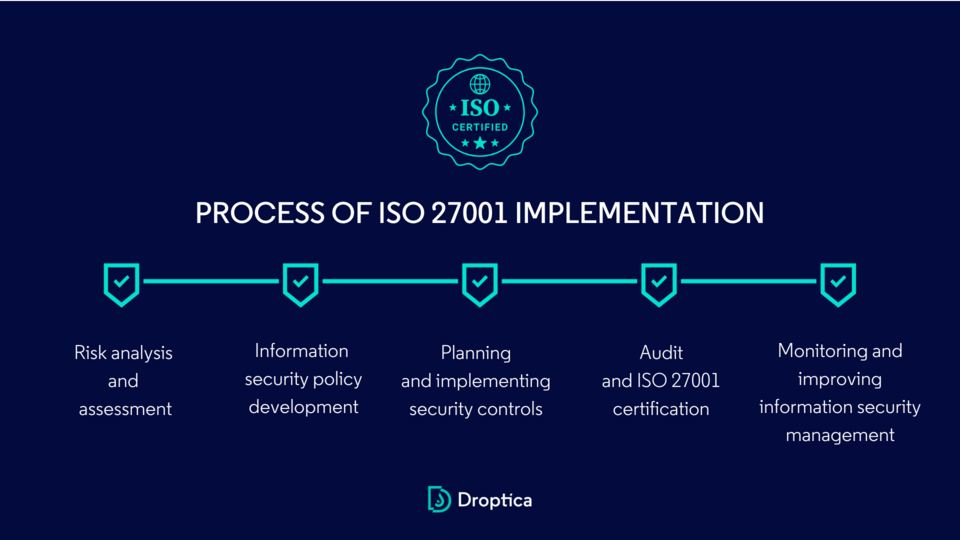
Key Benefits of ISO/IEC 27001:
- Risk Management: Helps identify and mitigate potential cyber risks.
- Compliance: Assists in meeting legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements.
- Reputation: Enhances trust with customers and stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to security.
Other Cyber Security Frameworks
Apart from ISO/IEC 27001, several other frameworks guide organizations in enhancing their cyber security posture:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework provides a policy framework for private sector organizations to assess and improve their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber attacks. The NIST framework consists of five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover, which offer a holistic approach to managing cyber security risks.
- GDPR Compliance: The General Data Protection Regulation is a regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy, crucial for companies handling EU citizens’ data. GDPR emphasizes stringent data protection requirements and mandates organizations to ensure the privacy and protection of personal data.
Global Cyber Security Regulations
Cyber security regulations vary by country, but there is a growing trend towards adopting international standards to ensure consistency and reliability in security practices. For instance:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Enforced in the European Union, GDPR is one of the most stringent regulations for data protection and privacy. It mandates organizations to implement robust security measures to protect personal data.
- CISA (Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act): In the United States, CISA encourages the sharing of cyber threat information between the government and private sector to enhance collective security.

Best Practices for Cyber Security
Adopting international standards and frameworks is only part of the solution. Organizations should also follow best practices to enhance their security posture:
- Regular Audits: Conducting cyber security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. These audits assess the effectiveness of the implemented security controls and ensure compliance with the established standards.
- Training and Awareness: Educating employees about cyber security policies and protocols is crucial. Regular training sessions can help staff recognize and respond to potential security threats, reducing the risk of human error.
- Incident Response Plan: Having a plan in place to respond to cyber incidents can minimize damage and recovery time. An effective incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken during a security breach, including communication strategies, containment measures, and recovery procedures.
Cyber Security Certification
Achieving cyber security certification, such as ISO 27001, demonstrates an organization’s commitment to securing its information. The certification process involves a thorough audit by a certified body to ensure compliance with the standard’s requirements. This process includes:
- Gap Analysis: Identifying areas that need improvement before the certification audit.
- Implementation: Applying the necessary changes to meet the standard’s requirements.
- Certification Audit: An external auditor evaluates the organization’s ISMS to verify compliance and award the certification.
The Role of Cyber Security Governance
Effective cyber security governance involves setting up a structure to oversee the implementation and monitoring of cyber security strategies. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing policies, and ensuring continuous improvement. Key components of cyber security governance are:

- Leadership Commitment: Top management must support and provide resources for cyber security initiatives.
- Policy Development: Creating comprehensive security policies that cover all aspects of information security.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly reviewing and assessing the effectiveness of the cyber security measures in place.
Cyber Security Strategy and Implementation
Developing a robust cyber security strategy involves:
- Assessing Risks: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities. This involves conducting risk assessments to understand the impact and likelihood of different cyber threats.
- Implementing Controls: Establishing appropriate security measures. This includes technical controls (e.g., firewalls, encryption) and administrative controls (e.g., policies, procedures).
- Monitoring and Reviewing: Continuously evaluating the effectiveness of security controls and making necessary adjustments. Regular reviews and updates ensure that the security measures remain effective against evolving threats.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing international cyber security standards is vital for protecting information and managing cyber risks. By following frameworks like ISO/IEC 27001 and adhering to global regulations, organizations can enhance their security posture, comply with legal requirements, and build trust with their stakeholders.
Implementing these standards not only mitigates risks but also demonstrates a proactive approach to cyber security, fostering a culture of security within the organization.
